|
Global Aircraft -- RQ-1 Predator
Aviation Center
US Attack
US Bombers
US Cargo
US Fighters
US Helicopters
US Patrol/Pursuit
US Reconnaissance
US Tankers
US Trainers
US UAV's
US X Planes
Orbiter Vehicles
WWI Aircraft
WWII Aircraft
Airbus
Antonov
Boeing
Dassault
Ilyushin
Kamov
MiG
Mil
Saab
Sukhoi
Tupolev
Yakovlev
Joint/Rest of World
Entertainment Center
Members Center
New Technologies
Contact Us
Extra Navigation
GAC Engine
RQ-1 Predator Specifications
RQ-1 Predator Achievements
RQ-1 Predator Features
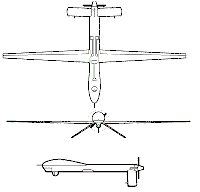
The RQ-1A/B Predator is a system, not just aircraft. A fully operational system consists of four aircraft (with sensors), a ground control station (GCS), a Predator Primary Satellite Link (PPSL), and 55 personnel for continuous 24 hour operations. The basic crew for the Predator is one pilot and two sensor operators. They fly the aircraft from inside the GCS via a C-Band line-of-sight data link or a Ku-Band satellite data link for beyond line-of-sight flight. The aircraft is equipped with a color nose camera (generally used by the aerial vehicle operator for flight control), a day variable aperture TV camera, a variable aperture infrared camera (for low light/night), and a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) for looking through smoke, clouds, or haze. The cameras produce full motion video and the SAR still frame radar images. The three sensors are carried on the same airframe but cannot be operated simultaneously. In the future, Predators will carry the Multispectral Targeting System (MTS) with inherent AGM-114 Hellfire missile targeting capability, and integrates electro-optical, infrared, laser designator and laser illuminator into a single sensor package. These Predators cannot carry MTS and the SAR simultaneously. The aircraft will carry and employ two laser-guided Hellfire anti-tank missiles with MTS. Each Predator aircraft can be disassembled into six main components and loaded into a container nicknamed "the coffin." This enables all system components and support equipment to be rapidly deployed worldwide. The largest component is the GCS and it is designed to be rolled into a C-130. The air transportable PPSL consists of a 6.25 meter Ku-Band satellite system mounted on a trailer. It provides communications between the ground station and the aircraft when it is beyond line-of-sight and is a link into secondary intelligence dissemination networks. The RQ-1B system needs 5,000 feet by 125 feet (1,524 meters by 38 meters) of hard surface runway with clear line-of-sight to each end from the GCS to the air vehicles. The RQ-1B includes an ARC-210 radio, an APX-100 IFF/SIF with Mode 4, an upgraded turbo-charged engine and an ice mitigation system. Source: http://www.af.mil
RQ-1 Predator Background
The "R" is the Department of Defense designation for reconnaissance; "Q" means unmanned aircraft system. The "1" refers to it being the first of a series of purpose-built unmanned reconnaissance aircraft systems. An "A" or "B" that follows the 1 states the version of the RQ-1 system series. The Predator system was designed in response to a Department of Defense requirement to provide persistent intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance information to the warfighter. It was the first successful advanced concept technology demonstration. This is a new acquisition process designed to reduce costs and development time by relying on commercial-off-the-shelf and government-off-the-shelf technology to the maximum extent possible. In April 1996, the secretary of defense selected the U. S. Air Force as the operating service for the RQ-1A Predator system. Operating responsibility is at the 11th, 15th and 17th Reconnaissance Squadrons, Indian Springs Air Force Auxiliary Field, Nev. Source: http://www.af.mil | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||